Understanding Basic Accountancy
- By Albert Madison
- •
- 30 Apr, 2018

Accountancy is
a branch of science that deals with financial aspect of a business. Mostly,
accounting deals with record keeping, analysis of business information,
interpretation of financial information and dissemination of accounting
information of a company to business owners and other people who has an
interest with the company.
Accountancy is a broad subject and has many
branches such as financial accounting, which enables business owners to have an
overview of the state of the business; cost accounting, which deals with
identifying, gathering and tracing of cost information to cost objects;
management accounting, which is almost similar to cost accounting; auditing,
which deals with the company’s credibility in terms of its financial
information; and taxation, which is known as the extension of business law.
In Singapore,
basic accounting course is being offered by different institutions. This
course teaches the fundamental accounting principles and can be taken by people
who has no prior background of accounting or bookkeeping. In addition to that,
any person who wanted to gain some knowledge on the aspects of basic accounting
can enroll to this course.
What will
I learn in basic accounting?
Income
statement
Income statement is a financial record that
shows how profitable a business is during a specific period. This period can be
a week, a month, or a year. The income statement shows two things: the revenue
(or the amount that was earned) and the expenses. You’ll learn how to create
income statements through basic
accounting courses.
Balance
Sheet
Balance sheet is a financial statement that
shows the company’s assets, liabilities and stockholders’ equity during a
specific period.
Assets are the things that company owns or the
resources of the company. Accounts receivable and prepaids are also assets of
the company.
Liabilities are things that the company has not
been paid for or are the amounts that the company owed to others. Examples of
liabilities are loans, the interest of the loan and wages.
Equity
The third section of a balance sheet of a
corporation is called stockholders’ equity, whereas those of a sole proprietorship
is called owner’s equity. Simply put, equity is the difference of assets minus
its liabilities or what is often called the book value.
Stockholders’ equity tackles concepts such as
common stock, paid-in capital in excess of par value-common stock, preferred
stock, retained earnings, treasury stock and current year’s net income.
Statement
of Cash Flow
The statement of cash flow shows the cash
generated and the cash used by the company’s operating activities, investing
activities and financing activities.
Double-Entry
System
Double-entry system is a record based on the
fact that every transaction has effects on at least two different accounts.
This system satisfies the basic accounting equation where assets is equal to
liabilities plus equity.
In the general ledger, the left side contains
the debit or the company’s asset. However, the right side of the general ledger
contains the credits or the company’s liabilities or equities. As an example,
if the company receives cash, the account is debited; whereas if the company
pays cash, the account is credited.
Basic accounting courses in Singapore that is offered by different institutions will tackle more about the fundamentals of accounting. The aforementioned terms are just an overview of what the syllabus will tackle.
I tried to recall what I learned during my time, uh, Punnett Square? Was that even chemistry? Anyways, in this article, I would tell you about the problem and how we made it work with the best chemistry tuition in Singapore : The Chemistry Practice.
As many parents in this situation can attest, this doesn’t happen overnight. For a kid, failing school is a progression of missed assignments, skipping classes and failed tests. As a parent, we need to address the problem quickly and get your child back on track before he or she becomes completely derailed.
Identify the problem
I understand that there could be several reasons my child is struggling. So, your child might not understand the material, could be struggling managing time between schoolwork and sports, or just might not be doing the work.
Her chemistry tutor says the most common struggle she sees is that kids are simply not trying hard enough. They just don’t put in the mental effort required to learn the material, either during class or at home, she explains.
I also noticed that during this era of schooling is often the first time a student has been challenged. It’s the first time school isn’t easy, and they don’t know how to handle that. I guess they don’t know how to study, so they are reluctant to do the practice and give the attention needed to understand what is confusing. As a student before myself, I know that students simply do not want to study. Too many students show up late for class, don’t bring materials, don’t turn in homework, and don’t study for tests.
Thankfully, my kid is not one of the many students who struggle with issues at home, which impact their overall academic performance. Therefore, I first had to identify if the problem stems from a lack of understanding, a lack of motivation, or a personal issue.
My daughter simply seemed to favour the creative side of her brain, she likes arts and history more than science and math. I wanted to hug her, it wasn't her fault. Learning can be different for each child.
Whatever the issue is for your child, it’s important to seek the assistance of an online A-level chemistry tutorbefore the problem spirals out of control.
Getting help
I scheduled an appointment with my kid's chemistry tutor. Then she later notifies me when my student is doing worse by a grade or two when compared to past performance. I am lucky because there are some tutors who reach out to a failing student before contacting the parent. In a one-on-one, the tutor I hired addresses the problem, trying to find the reason for the failing grade of my kid, and then set up a game plan to get her back on track on her Chemistry periodic table.
The tutor also suggested additional resources to assist my child. For example, Lakeview High School offers free-of-charge peer tutoring and teacher tutoring during the school week – both before and after school. The Chemistry Practice seems to encourage kids to take advantage of any of the study assistance available at their school, and it works.
Tips for parents
Be proactive. If you know your kid falls behind in his or her schoolwork or doesn’t do so well when it comes to grades, talk to the teacher immediately – before it becomes an issue in that class. I am one of those parents who email the tutor every week to check up on assignments, their progress or behaviour, and even things that are going on at home that might be affecting my kid.
Make your expectations clear and stick with them. Did your daughter’s grades drop? It’s time to take away some of her privileges. Get in contact with her tutor, too, and inform the instructor of the expectations you’ve set for your child.
Attend parent-teacher conferences. Students whose parents regularly attend conferences tend to perform better in school. Strengthening the parent-teacher bond and get some tips for parent-teacher conferences to help you in this arena.
Use online grade books. All schools provide personalized logins for parents and guardians. Inform your kids that you’re checking on their grades and contact teachers if you have questions or concerns.
The bottom line
When it comes to what to do when our child is failing school, turning bad grades into good grades is a group effort among parents, teachers, and students. We parents need to be part of their children’s education. As a parent, the best thing you can do is be involved, be consistent, be supportive and be patient.
So, if you need to enrol your kid to H2 chemistry tuition, visit The Chemistry Practice's website here, and let their tutors help your kids today.The body content of your post goes here. To edit this text, click on it and delete this default text and start typing your own (or paste your own from a different source).
To control the color or size of this text, please change the global colors or text size under the Design section from the left menu of the editor.
When you realise the true value of tuition school, you’ll have to consider your budgeting plan and make sure all your kids can attend. But, what actually are you paying for in a tuition school?
As a primary English tuition in Singapore, we enlighten you further on what you’re paying for when you decide to sign up your kids to our programmes:
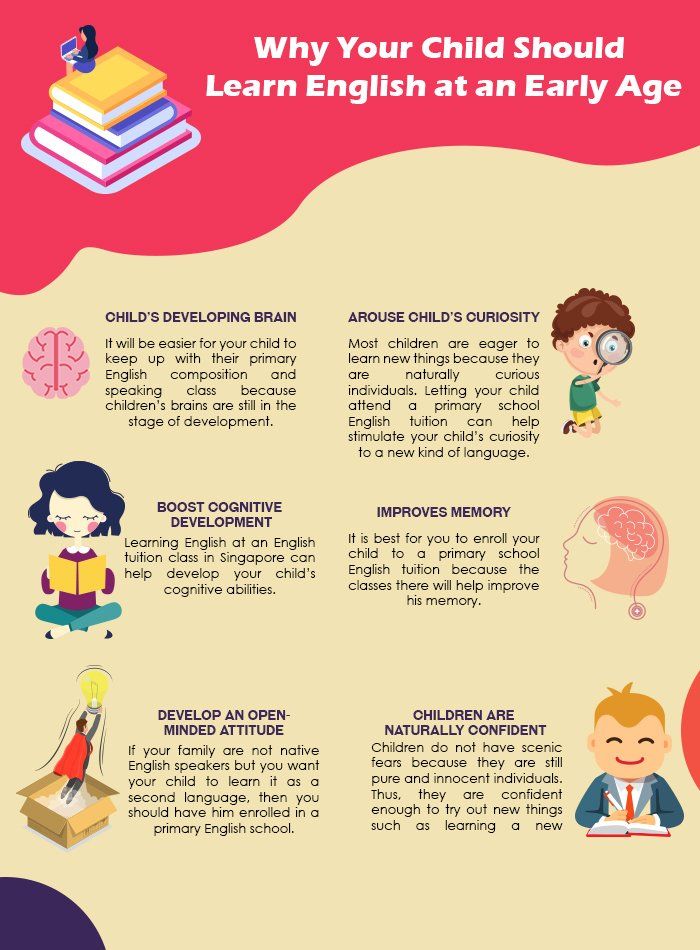
Small-Sized Classes
As a private tuition centre, we strive to keep our classes small to make sure that our students get the attention that they deserve. Unlike in a large classroom, our teachers don’t have to split their time between keeping the other students busy and preventing a few from failing the class. Everyone is guaranteed to be provided with individual support they’re just not going to get in a busy classroom.
Fluent and Native English Speaking Teachers
Here at Lil’ But Mighty, we take pride in having a set of teachers who, if not native speakers, are fluent in speaking the language. These professionals understand the language on a higher level hence, we can guarantee that our students will learn conversational English on top of textbook English. It means when you enrol your kids in our programme, they’ll be constantly guided by teachers who are fluent in English.
Additional Support in their Regular Classes
When you shell out cash for an English tuitionschool, you not only play for help at the session or for the time someone will look after your kids. Instead, you pay for tuition so your child could be equipped with advanced learning, study tips and tricks that they will carry into their regular classroom. This new-found knowledge will help your kids keep up, if not get ahead of their studies, as well.
Lifelong Advantage
Now, the benefits you can get in spending for your kids’ tuition don’t end in their classrooms. Whatever your child wants to be when they grow up, you provide them with valuable educational support that will be useful no matter the career path they will take. There’s hardly a field of work where fluency in English and advanced grades will not be impressive.
If you’re contemplating to send only one of your kids to English class tuition—either one who is struggling the most or the one you think will succeed the most—just think of how the rest will see it. When one gets singled out, it may appear as favouritism to your other kids.
It may be expensive at first, but keep in mind that you get what you pay for. We promise you that it will all be worth it in the end!
If you’re looking to learn more about our programmes, get in touch with us today!

By being with a H2 Physics tuitioncentre tutor, gain a better understanding of the topic.